Fertilizer: Why It’s More Important Than You think
The global population is expected to reach nearly 10 billion people by 2050. So, in order to feed our growing world sustainably, increased crop production is essential.
Over recent decades, farmers have been able to more than double their production of crops thanks to fertilizers and the vital nutrients they contain.
When crops are harvested, the essential nutrients are taken away with them to the dining table, resulting in the depletion of these nutrients in the soil. To replenish these nutrients, fertilizers are needed, and the cycle continues.
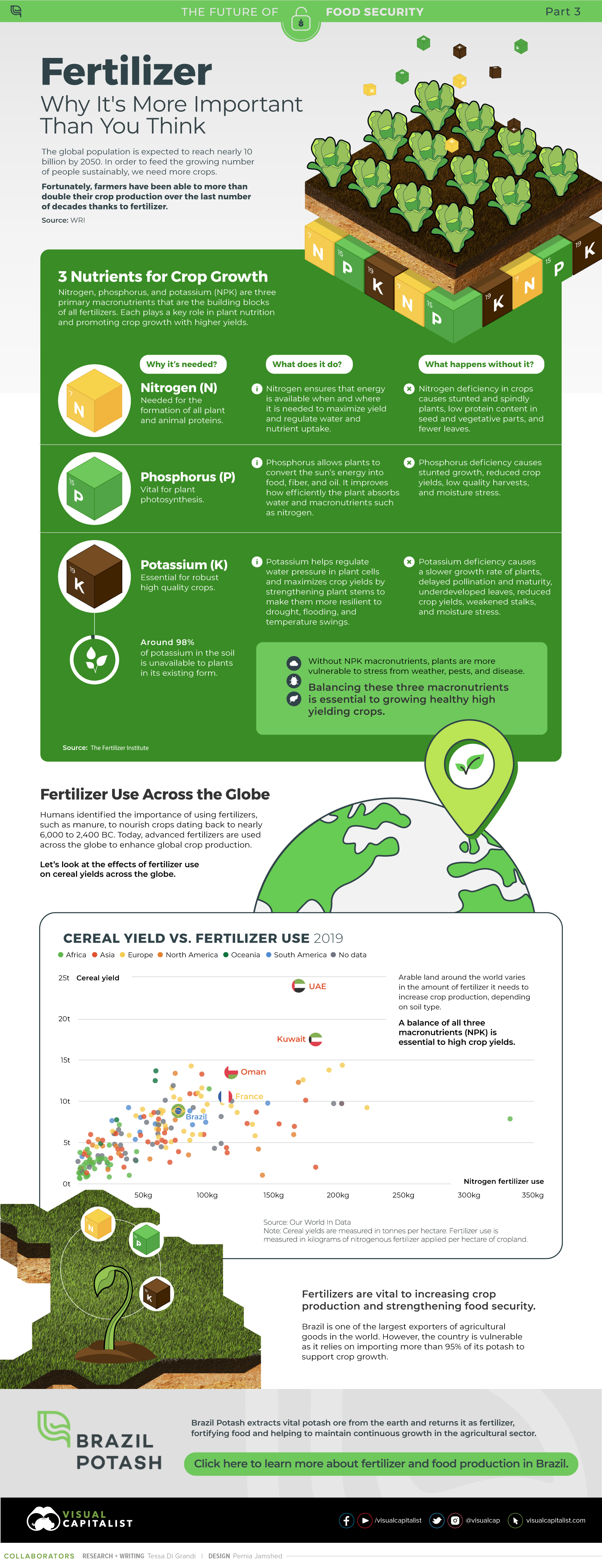
The above infographic by Brazil Potash shows the role that each macronutrient plays in growing healthy, high-yielding crops.
 Sharp rebound in Urea raises questions over fertilizer prices bottoming out.
Sharp rebound in Urea raises questions over fertilizer prices bottoming out.
Food for Growth
Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK) are three primary macronutrients that are the building blocks of the global fertilizer industry. Each plays a key role in plant nutrition and promoting crop growth with higher yields.
Let’s take a look at how each macronutrient affects plant growth.
| Nutrient | Why it’s needed? | What does it do? | What happens without it? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N) | Needed for the formation of all plant and animal proteins. |
Nitrogen ensures that energy is available when and where it is needed to maximize yield and regulate water and nutrient uptake. |
Nitrogen deficiency in crops causes stunted and spindly plants, low protein content in seed and vegetative parts, and fewer leaves. |
| Phosphorus (P) | Vital for plant photosynthesis. |
Phosphorus allows plants to convert the sun’s energy into food, fiber, and oil. It improves how efficiently the plant absorbs water and macronutrients such as nitrogen. |
Phosphorus deficiency causes stunted growth, reduced crop yields, low quality harvests, and moisture stress. |
| Potassium (K) | Essential for robust high quality crops. |
Potassium helps regulate water pressure in plant cells and maximizes crop yields by strengthening plant stems to make them more resilient to drought, flooding, and temperature swings. |
Potassium deficiency causes a slower growth rate of plants, delayed pollination and maturity, underdeveloped leaves, reduced crop yields, weakened stalks, and moisture stress. |
If crops lack NPK macronutrients, they become vulnerable to various stresses caused by weather conditions, pests, and diseases. Therefore, it is crucial to maintain a balance of all three macronutrients for the production of healthy, high-yielding crops.
The Importance of Fertilizers
Humans identified the importance of using fertilizers, such as manure, to nourish crops dating back to nearly 6,000 to 2,400 BC.
As agriculture became more intensive and large-scale, farmers began to experiment with different types of fertilizers. Today advanced chemical fertilizers are used across the globe to enhance global crop production.
There are a myriad of factors that affect soil type, and so the farmable land must have a healthy balance of all three macronutrients to support high-yielding, healthy crops. Consequently, arable land around the world varies in the amount and type of fertilizer it needs.
Fertilizers play an integral role in strengthening food security, and a supply of locally available fertilizer is needed in supporting global food systems in an ever-growing world.
Brazil is one of the largest exporters of agricultural goods in the world. However, the country is vulnerable as it relies on importing more than 95% of its potash to support crop growth.
Brazil Potash is developing a new potash project in Brazil to ensure a stable domestic source of this nutrient-rich fertilizer critical for global food security.














