On a summer day several years ago, Fabrice Lambert, a climatologist at the Pontifical Catholic University of Chile, met one of his colleagues in Quinta Normal, a 35-hectare public park in central Santiago.
In September each year, South Africa's Gauteng province turns purple.
If a tree falls in the forest, will another replace it?
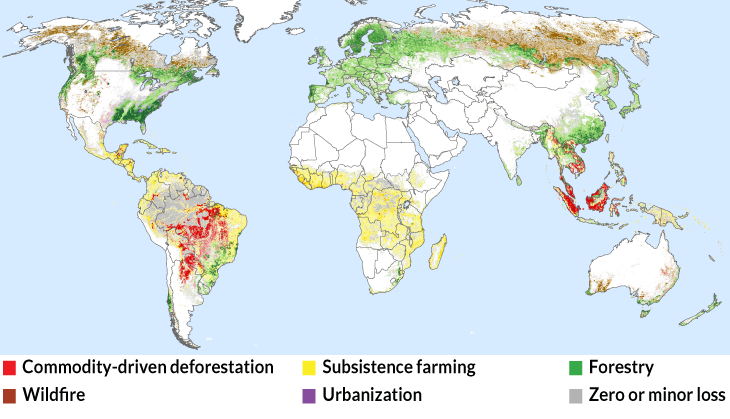
Of the roughly 3 million square kilometers of forest lost worldwide from 2001 to 2015, a new analysis suggests that 27 percent of that loss was permanent — the result of land being converted for industrial agriculture to meet global demand for products such as soy, timber, beef and palm oil.
he tiny polyphagous shot hole borer and its associated fungus looks set to become the most damaging biological invasion in South Africa’s urban environments, warns the country’s latest report on biological invasions.
Scientists around the world are looking for ways to remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This gas is a natural component of the atmosphere, released by processes of respiration and decomposition of organic matter.
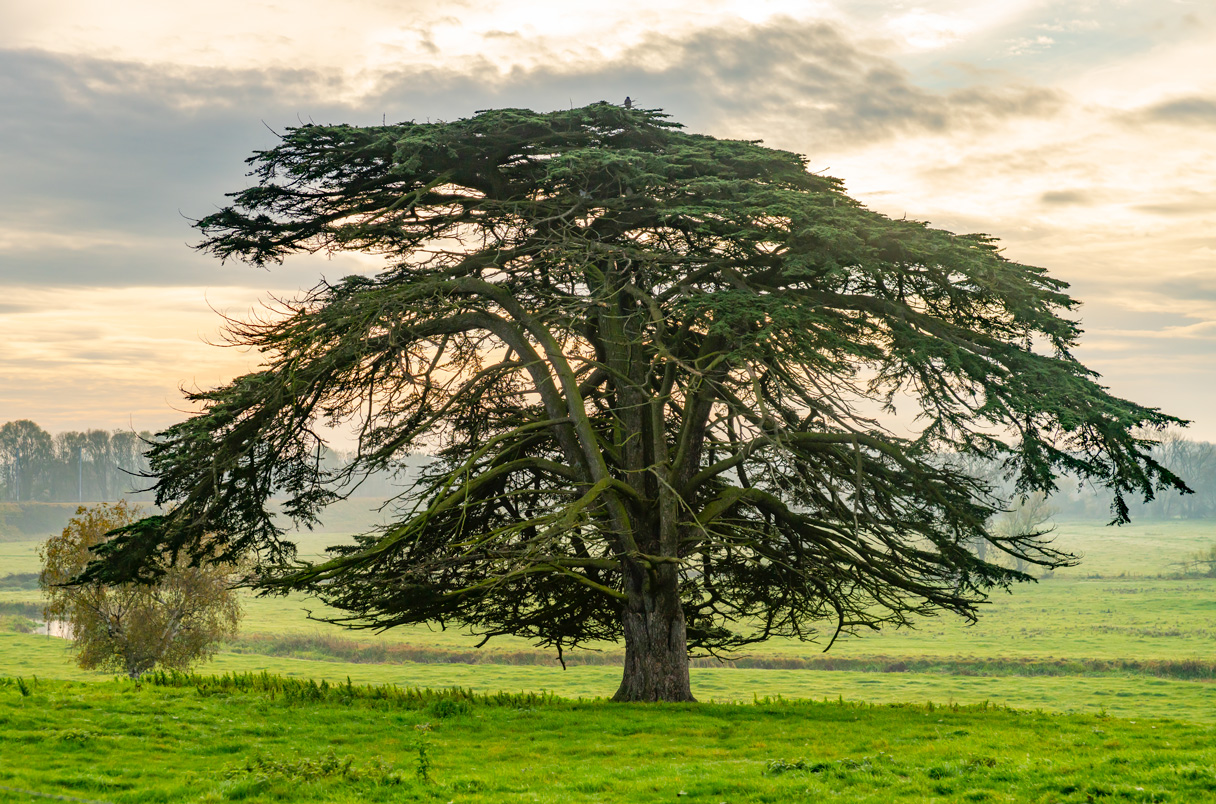
The biggest trees capture the most carbon: Large trees dominate carbon storage in forests
- Hits: 3198
Older, large-diameter trees have been shown to store disproportionally massive amounts of carbon compared to smaller trees, highlighting their importance in mitigating climate change, according to a new study in Frontiers in Forests and Global Change.
Newsletter Subscribe
AGRI NEWS NET "LIVE" FEED
- CRA Media independence is the absence of external control and influence of any other media. Our capacity is to "make decisions and act according to its logic," and distinguishes us from the vast majority of media- Committed, focused and always on time- Good positive News you can trust- We not part of the negative sensational news media of the 2025 century.
- This is AGRI NEWS NET- the world of Farming and Agriculture in your hand. "Good" News you can Trust- Updated 7 days a week- bringing you the latest News in Farming and Agriculture from all over the world. Tomorrow at 6 AM South African time you can start browsing again.
- First things first, scotch is actually a whiskey, er, whisky. Whiskey is the spelling in the United States and Ireland. Whisky is the spelling in Canada, Japan, and Scotland. What sets Scotch whisky apart from other whiskies is that Scotch whisky is entirely produced and bottled in Scotland. There is no wrong way to drink Jameson Irish Whiskey but, we do ask you to drink responsibly.
- We have Over 1000 professional Audio cast recordings- Its very popular- Click on the link and follow us. Our Audiocast include a weekly AGRI RUSH- Headline s of the week.
Popular News Tags
AGRI NEWS NET AUDIO CAST Feeding-
- What Needs to Change in Farming and Agriculture in 2025
- AGRI NEWS RUSH - News Headlines of the Week 18/01/2025
- Farmer safety in South Africa in 2025
- The Economics of Farming and Agriculture in South Africa 2025
- The global wine market 2025
- AGRI NEWS RUSH - News Headlines of the Week 11/01/2024
- Artificial Intelligence: All That Glitters Is Not Gold
- GLOBAL WATER OUTLOOK TO 2025 Averting an Impending Crisis